Audit the system
Configure audit trail logging to review and to monitor Intelligence Center and system events.
To access the Audit view, you must have at least the following permissions:
read configurations
read audit-trail
All default Intelligence Center roles have the necessary permissions to access the Audit view.
View the audit trail
You can view audit logs in the Intelligence Center web-based interface, as well as in Kibana.
The Audit trail records events related to:
Entities: creation, modification, deletion, failed operations.
Datasets and workspaces: creation, modification — for example, adding or removing entities to and from a dataset, or elements to and from a workspace — deletion, failed operations.
Enrichers: execution status — for example, running or pending enrichment tasks — successful or failed execution completion.
Incoming and outgoing feeds: execution status — for example, running or pending ingestion and dissemination tasks — successful or failed execution completion.
Rules: execution status — for example, running or pending rule tasks — successful or failed execution completion.
Other tasks: for example, package or file upload and download; tag, taxonomy, user, and group creation, modification, and deletion.
Authentication: failed user account authentication attempts, two-factor authentication-related events, as well as user locking and unlocking.
It records:
Login attempts for unknown, inactive, and locked users
Amount of consecutive failed sign-in attempts by the same user.
Example: Bad password #1
Locking a user after exceeding the maximum amount of consecutive failed sign-in attempts.
Example: Bad password #3: user has been locked
Unlocking a locked user.
Only administrators can unlock locked users.
Example: Updated User (id:{user_id}}): user has been unlocked
View audit logs in the web interface
To view audit logs in the Intelligence Center web-based interface:
In the side navigation bar, go to Settings
 > System settings > Audit.
> System settings > Audit.Information in the Audit view relies on the Elasticsearch audit index.
If audit logging is enabled, and if the audit log file is populated, audit log records are returned.
Use the quick filters
 to look for specific audit records based on a date range, on one or more specific users, HTTP methods, or HTTP response status codes.
to look for specific audit records based on a date range, on one or more specific users, HTTP methods, or HTTP response status codes.To show and to hide the available quick filters in the current view click
 .
.To sort items by column header:
Click the header of the column whose content you want to sort.
Click
 or
or  to sort the content in either ascending or descending order, respectively.
to sort the content in either ascending or descending order, respectively.
|
Filter |
Description |
|
Timestamp |
Displays the search result items included in the specified time range. |
|
User |
Displays the search result items with the selected user name(s). |
|
Method |
Displays the search result items with the selected HTTP method(s): DELETE, POST, PUT. |
|
Response |
Displays the search result items with the selected HTTP response status code(s): 2xx, 4xx, or 5xx. |
|
Path |
The API endpoint acting as an interface to invoke the task or service being audited. Example: /private/entities/ |
|
Message |
An informative message describing the type of event: for example, an update, a modification, a failed sign-in attempt, and so on. |
View audit logs in Kibana
You can view audit log information also by selecting specific indices in Kibana.
Access Kibana
To access Kibana:
In the web browser address bar enter a URL with the following format:
https://${platform_host_name}/private/kibana/app/kibana#Keep the trailing #
Example: https://eclecticiq.platform.org/private/kibana/app/kibana#
View logs in Kibana
In Kibana select Discover.
In the Discover view select one of the following indices:
audit*: audit trail index.
It records events related to entities, datasets, enrichers, incoming and outgoing feeds, rules, tasks, and failed user account authentication attempts.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
method:DELETE; username:kmitnick; message:Deleted*
To select this index in the Intelligence Center GUI, in the side navigation bar click
 > System settings > Audit to display the Audit tab.
> System settings > Audit to display the Audit tab.logstash*: it records log information related to ingestion, tasks, and task scheduling.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
*event:entities.stored; level:error; logger:eiq.platform.ingestion; tags:ingestion
statsite*: it collects metrics about ingested and received packages, invalid or not well-formed lines in the ingested packages, as well as ingestion speed and performance.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
grp:packets_received; grp:bad_lines_seen
If audit logging is enabled, the selected audit* index returns audit log records within the specified time range.
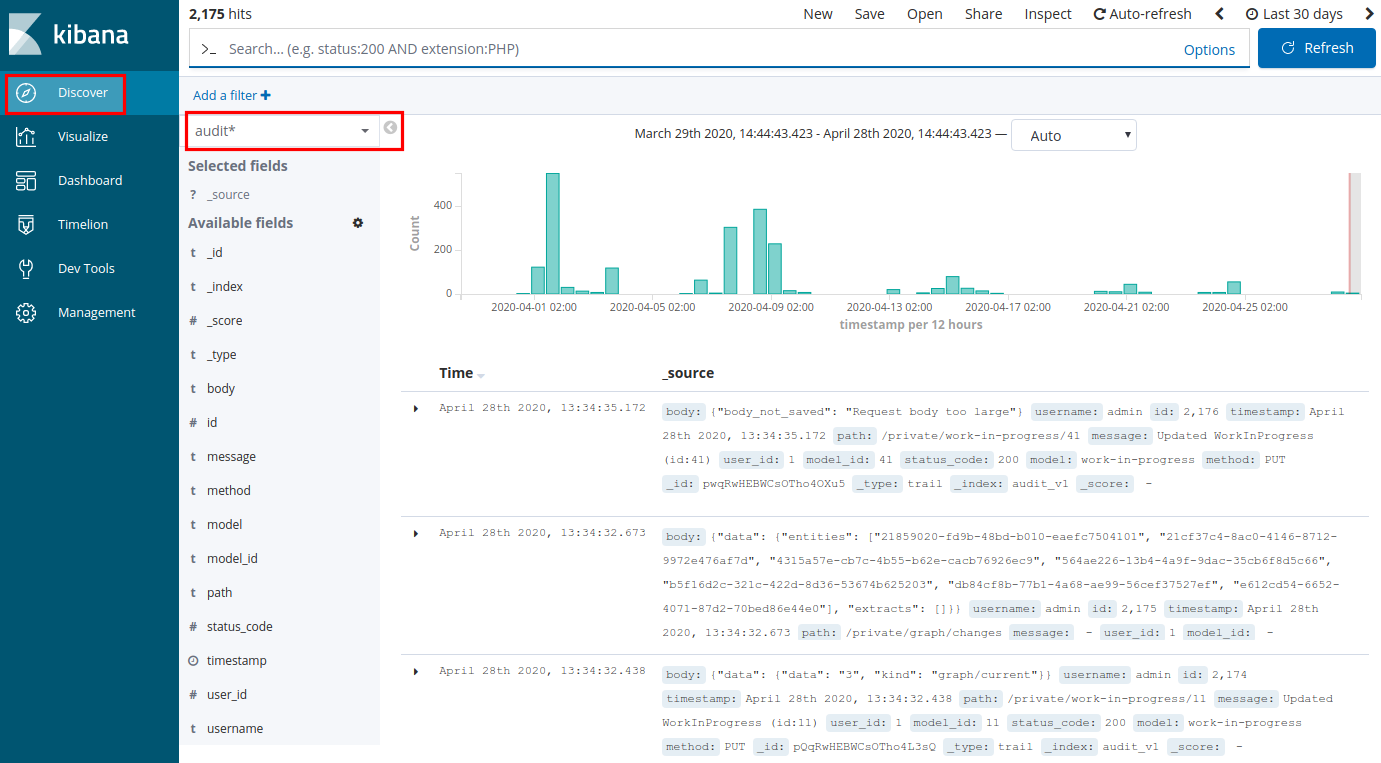
The request payload for an audit log entry cannot exceed 4 KB.
If the request body in the request payload for an audit log entry is larger than 4 KB, the following message is displayed:
"Request body too large"# Raw JSON key/value pair:"body": "{\"body_not_saved\": \"Request body too large\"}"Search audit logs in Kibana
In Kibana select Discover.
In the Discover view select the following index:
audit*: audit trail index.
It records events related to entities, datasets, enrichers, incoming and outgoing feeds, rules, tasks, and failed user account authentication attempts.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
method:DELETE; username:kmitnick; message:Deleted*
Set the update interval
By default, the log data time range search interval is set to 15 minutes: queries search for matches in logs dating from the last 15 minutes until the present time.
To adjust the time interval, in the top-right corner click the clock icon  , and choose an appropriate time range for the search.
, and choose an appropriate time range for the search.

statsite_index_kibana_time_range.png
Search by level
Log records are assigned a severity level. In this way, you can filter searches to retrieve only errors, warnings, or informative/notification log records.
To run a search by severity level in Kibana:
In Kibana select Discover.
In the Discover view select the following index:
logstash*: it records log information related to ingestion, tasks, and task scheduling.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
*event:entities.stored; level:error; logger:eiq.platform.ingestion; tags:ingestion
Enter this in the Kibana search bar…
…to obtain this result
level:"error"
Returns all logging errors.
level:"warning"
Returns all logging warnings.
level:"info"
Returns all logging information and notifications.
Search by tag
Log records are tagged, so that you can identify the Intelligence Center component a log refers to.
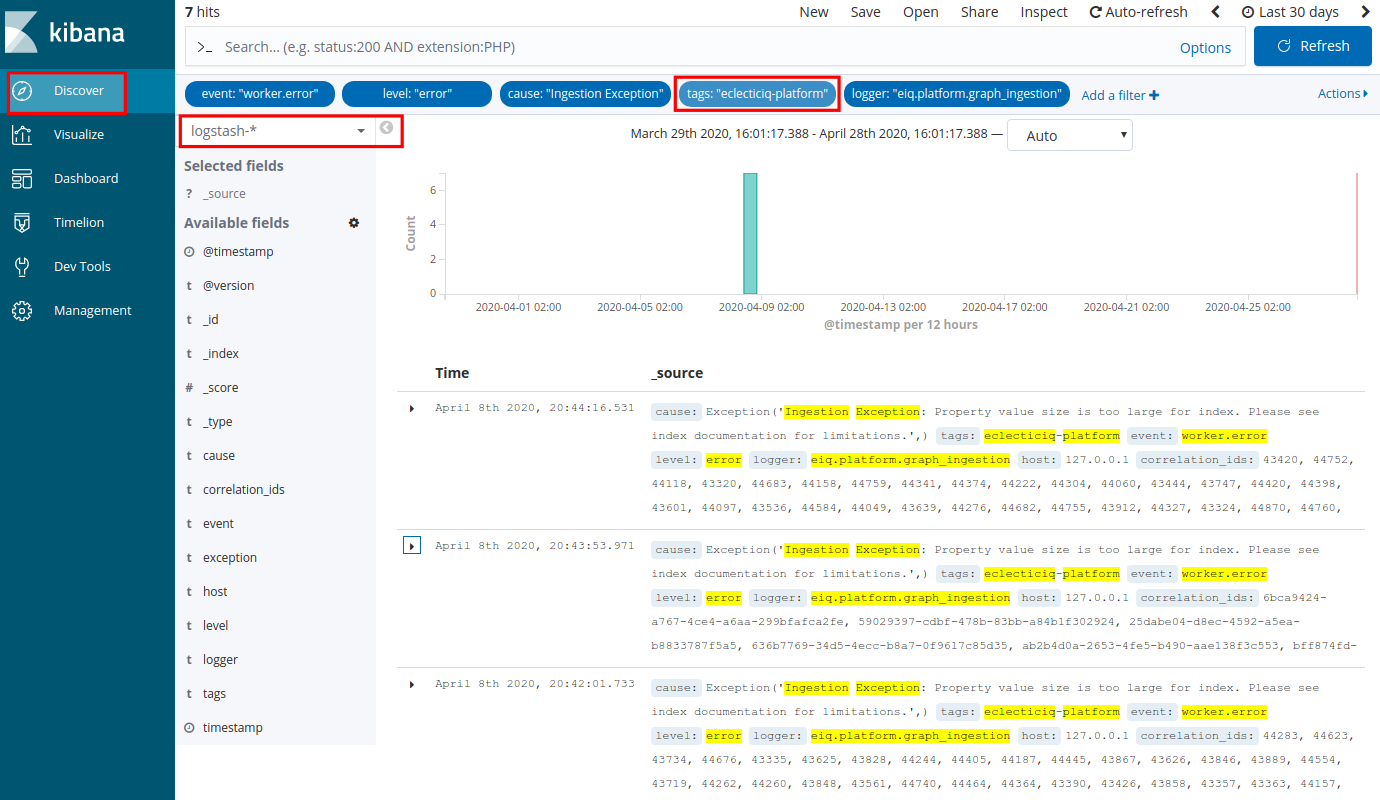
To run a search by tag in Kibana to look for issues or information about a specific component:
In Kibana select Discover.
In the Discover view select the following index:
logstash*: it records log information related to ingestion, tasks, and task scheduling.
You can search for specific subsets by entering key/value pairs in the search input field.
Example:
*event:entities.stored; level:error; logger:eiq.platform.ingestion; tags:ingestion
In the Kibana search bar enter this…
…to get this result
tags:"ingestion"
Returns logs related to the intelligence ingestion module controlling how the Intelligence Center ingests source data.
tags:"opentaxii"
Returns logs related to the EclecticIQ OpenTAXII server implementing the TAXII services.
tags:"platform-api"
Returns logs related to the EclecticIQ Intelligence Center API.
tags:"task-workers"
Returns logs related to services and workers carrying out backend and background tasks related to, for example, scheduling, reindexing, and prioritization.
Search with Boolean operators
You can use Boolean operators to refine your search and zero in on specific log types or components.
For example, you can search for graph ingestion issues by entering the following query in the Kibana search input field:
level: "error" AND cause: "Ingestion Exception" AND logger: "eiq.platform.graph_ingestion"You can search for graph ingestion timeout issues by entering the following query in the Kibana search input field:
level:"error" AND exception:"BATCH_INGESTION_TIMEOUT" OR logger: "eiq.platform.graph_ingestion"